Table of Contents
What is Titration?
Neutralisation Real Life Examples
How to do Titration?
How did you get the Results at number 4?
Neutralisation Real Life Examples
How to do Titration?
What is Neutralisation?
Neutralisation is a process, in which when an
acid
is added to
base or alkali
to produce salt and water.
Neutralisation can be done in Laboratory. The process is called
Titration.
The apparatus used in Titration are :
- Retord Stand and Clamp
- Burette
- Conical Flask
- White Tile ( As Secondary Apparatus )
And the Materials used in Titration are :
- Acid
- Alkali
- Indicator
Lets say Hydrochloric Acid is our Acid, and Sodium Hydroxide is our
Alkali.
General Equation :
Word Equation :
Hydrochloric Acid + Sodium Hydroxide → Sodium Chloride + Water
Chemical Equation :
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
Some of the real life examples of Neutralisation are :
| Cause | What is used to treat |
|
Bee sting
( Acidic )
|
Soap, Toothpaste or Baking Soda
( All of it are Alkaline )
|
|
Wasp Sting
( Alkaline )
|
Lemon, Lime or Vinegar
( All of it are Acidic )
|
|
Gastric ( Too much acid in stomach )
( Acidic )
|
Antacid ( A.K.A Milk of Magnesia )
( Antacid is Alkaline )
|
|
Acidic Soil
( Acidic )
|
Spray Lime ( A.K.A Calcium Hydroxide )
( Lime is Alkaline )
|

|
| A brand for Milk of Magnesia |
Next, we move on to Neutralisation in laboratory.
Neutralisation in laboratory has a name, but not called as "Neutralization in Laboratory", it is called Titration. The Apparatus used are as shown here, and the word equations are as shown here.
To achieve Titration, there is only 5 somehow easy steps. These steps
are shown below :
Repeat procedure 2 to 3 times for accuracy.
- Titrate Acid into Alkali and Indicator.
- Wait till it reaches the Neutralisation point ( pH 7, as shown on indicator )
- Repeat Procedure 1 to 2 for 3 times to get a more accurate result. Add the number from the 3 tries and divide it by 3 to get the average amount of acid to neutralise alkali.
- Repeat without indicator
- Record all the results.
Here is an example in case you gotten the results and you don't know
what to do.
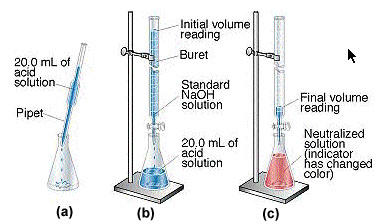
|
| Neutralisation, Set up as shown in the picture. |
Record the results like this :
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Alkali |
25 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
Acid |
23 |
24 |
23 |
23.33 |
How did you get the Results at number 4?
Simply divide Results at 1, 2, 3 together to get the results and that
would be the average!
Conclusion :
Acid + Alkali = NEUTRALISATION!
This is the end of Neutralisation
To go back to Homepage, click this link :
To go to Chemistry Element Website, click this link :
Thanks for visiting.
If there is any improvements needed, feel free to comment at the comment
section below.
Thank you.

No comments:
Post a Comment